- Best Antibiotics for Horse Wounds: What to Expect When Your Horse Has an Injury - September 20, 2023
- Bronco vs Mustang Horse: Are They the Same? - September 8, 2023
- Thoroughbred vs Quarter Horse - September 8, 2023
When you put Thoroughbred vs Quarter Horse side by side, you can easily spot the distinctive differences in their body build. But is it enough to decide which one will suit you better? Let’s look at what sets these two beautiful horse breeds apart in detail.
A Thoroughbred horse is known for its agility, grace, and strong spirit. I can still remember the thrill of riding a Thoroughbred for the very first time at the track, sensing its incredible power and classiness as we sprinted down the stretch.
The Quarter Horse, on the other hand, is more muscular with strong hindquarters. I’ve had the pleasure of owning one in the past, and I can say that it’s an incredibly versatile animal.
Both breeds certainly hold a special place in my heart, but I also understand that each of them has its limitations for different types of equestrians. This thorough comparison will answer all your questions and help you pick the best one for you.
Bottom Line Up Front
Thoroughbreds are a perfect match for riders interested in horse racing or any other activities involving acceleration and vigorous pace. However, these horses need a firm hand and are not suitable for beginners.
Quarter Horses have a milder temper. They are also incredibly versatile and make wonderful lifelong companions, so I’d recommend them even to less skilled riders.
Main Differences Between Thoroughbred vs Quarter Horse
The main differences between Thoroughbred vs Quarter Horse are:
- Thoroughbreds are slim, tall, and sleek, whereas Quarter Horses are thicker and more muscular.
- Thoroughbreds are spirited and lively, whereas Quarter Horses have a calm and mild temperament.
- Thoroughbreds are ideal for horse racing or show jumping, whereas Quarter Horses are more versatile.
- Thoroughbreds have better stamina for longer runs or rides, whereas Quarter Horses typically run out of energy faster.
- Thoroughbred is generally considered one of the most expensive horse breeds in the world, whereas Quarter Horse is more accessible even with a limited budget.
Key Characteristics: Thoroughbred vs Quarter Horse
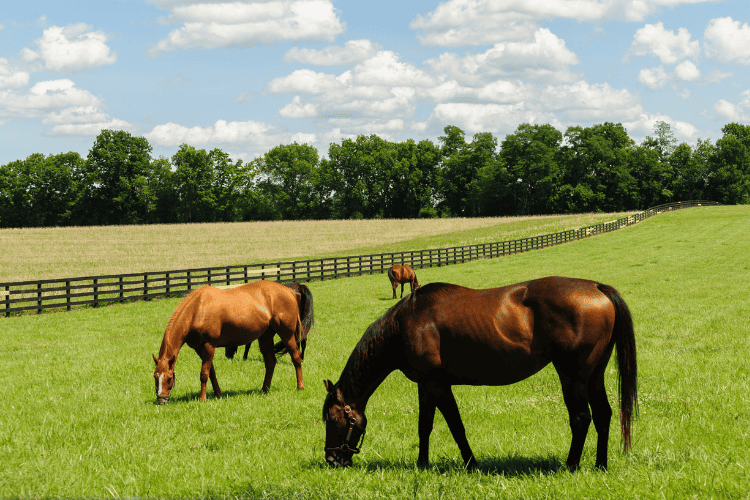

Thoroughbred and Quarter Horse are both excellent horse breeds with millions of admirers and happy owners worldwide. Nevertheless, each offers a bit different qualities.
Let’s compare the specific physical traits, genetic predispositions, temperaments, and origins of these two popular breeds side by side.
Thoroughbred vs Quarter Horse Characteristics Summary
| Characteristics | Thoroughbred | Quarter Horse |
| Aesthetics | Elegant slim appearance. Less distinctive mane and hair. Colors include grey, bay, chestnut, and black. There are roan thoroughbreds, too. | Thicker and shorter but still sleek. More voluminous mane and tail. Colors include sorrel, bay, palomino, black, buckskin, and overo or tobiano patterns. |
| Body build | Tall, slim bodies with well-defined muscles. 15 to 17 hands tall/900 to 1,200 pounds in weight. | More stocky, thicker bodies with robust hindquarters and dominant muscles. 14 to 16 hands tall/950 to 1,250 pounds in weight. |
| Genetics | Common joint and bone issues are caused by stress placed on the legs. Lung bleeding is also quite common. Lifespan between 25 and 30 years. | Prone to obesity and related health issues. Various hereditary metabolic issues are also quite common (HYPP, EPSM). Lifespan ranges from 25 to 35 years. |
| Temperament | Energetic, spirited, and sensitive, ideal for experienced riders with firm hands. | Calm, steady, and easily adaptable to new environments. It’s a good choice for less experienced riders. |
| Common use | Racing, show jumping, dressage, cross country, steeplechase, etc. | Western-style riding, rodeo, cutting reining, ranch work, pleasure riding, etc. |
| Price and requirements | Expensive horses with demanding day-to-day care. | Much more affordable horses with less specific care demands. |
| Origins | England, 17th century. | Colonial America, 17th century. |
Aesthetics

If you see a Thoroughbred and Quarter Horse side by side, you can spot differences in their appearance, even if you have no previous experience with horses in general.
Thoroughbreds are distinctively sleek and graceful, naturally attracting people focused on equines’ aesthetics. Their coat colors can range from grey or bay to chestnut and black. I’ve seen some beautiful roan Thoroughbreds in the past, too.
Thoroughbreds’ mane is typically shorter and very fine, lying flat over their necks. This allows their alert, rounded eyes and lovely long ears to stand out. Their tails are also relatively modest, lacking the volume of other breeds’ flashy tails.
Quarter Horses, on the other hand, sport fuller manes and tails, and their hair is often slightly curly and coarse. In my opinion, this makes them look a bit more raw and wild compared to Thoroughbreds, which can suit riders who prefer the more natural appearance of equines.
Quarter’s head is typically more robust, with a broad forehead and calm eyes. This horse can appear in many colors, including sorrel, bay, palomino, black, buckskin, and many more. I’ve even encountered some gorgeous overo and tobiano Quarter Horses.
(If you’d like to learn more about this topic in general, check out our horse colors guide!)
Body Build
Thoroughbreds have a distinctly athletic build, which is logical since they were primarily bred for speed and agility. They can be easily distinguished from many other breeds thanks to their long necks, lean legs, and the overall elegance of their beautifully defined muscles.
They usually stand around 15 to 17 hands tall (60 to 68 inches), but I’ve even seen some taller thoroughbreds.
Quarter Horses have a visibly stockier, more compact, and dominant presence. Their broad chests and strong hindquarters enable them to function well in many different situations and environments.
These horses are commonly between 14 and 16 hands (56 to 64 inches) tall, so they are usually slightly shorter than Thoroughbreds. The difference is, however, not very distinctive, so I would not consider it an essential factor when deciding between the two.
There’s a slight difference between the breeds’ weight, too. While Thoroughbred usually weighs from 900 to 1,200 pounds, Quarter Horses tend to be a bit on the heavier side due to their stocky build (950 to 1,250 pounds/430 to 567 kilograms).
Again, the difference is not huge, and you can often meet animals from either of these breeds that are lighter or heavier than these official averages.
Genetics

Thoroughbreds are adapted to horse racing, meaning their genetic traits lie mainly in their strong cardiovascular system, perfectly optimized for endurance and sprints.
These horses are known to have exceptionally well-developed fast-twitch muscle fibers, which are crucial for swift acceleration and quick direction changes.
On the other hand, Thoroughbreds are prone to various orthopedic issues, which is a typical issue with numerous racing breeds. Many Thoroughbreds I’ve had in my care in the past had joint problems and even fractures caused by the stress their legs had to endure.
Other common health issues with this breed include pulmonary hemorrhage (lung bleeding caused by excessive exercising) due to the intense physical demands of racing, as well as lameness and hoof pain.
A Thoroughbred can be expected to live up to 25 or even 30 years. However, they will likely need to retire much earlier from active racing.
The Quarter Horse’s lifespan is almost identical, although I’ve met a few animals above 30 years of age. Quarter Horses are less focused on speed, which is evident from their even mixture of fast-twitch and slow-twitch muscles. This genetic trait gives them excellent versatility and a good balance between persistence and speed.
Quarters don’t have so many issues with their joints or bones, but their robust build makes them more prone to obesity, which comes hand-in-hand with various metabolic problems.
I’ve seen several of these horses suffering from hyperkalemic periodic paralysis (HYPP), a hereditary muscle disorder demonstrated by muscle tremors or even complete paralysis.
I’ve also heard Quarter Horses are prone to polysaccharide storage myopathy (EPSM), another metabolic disorder concerning muscles and movement in general.
Temperament
Thoroughbreds are typically strong-willed or even hot-headed animals, which can be too much for an inexperienced rider. I’ve met a few pretty mischievous Thoroughbreds who could drive even a professional trainer crazy with their stubbornness.
These animals can also be very sensitive, especially in a foreign environment or around strangers, so they also require a large amount of patience and empathy.
Nevertheless, they are a perfect match for competitive riders focused on results since their work ethic, energy, and willingness to excel are unparalleled.
Quarter Horse makes a much better horse breed for beginners. These animals are usually very calm, thoughtful, stable, and predictable (in the best sense).
They are known to adapt to new situations or environments very quickly, hardly ever showing any restlessness or agitation. This can be very helpful if you’re, for example, planning to acquire an older animal or to retrain a horse for a completely new use, discipline, or race.
Quarter Horses are your best choice if you’re looking for a cooperative and friendly equine that would let you go away with a few beginner mistakes or lack of strictness during training.
Common Use
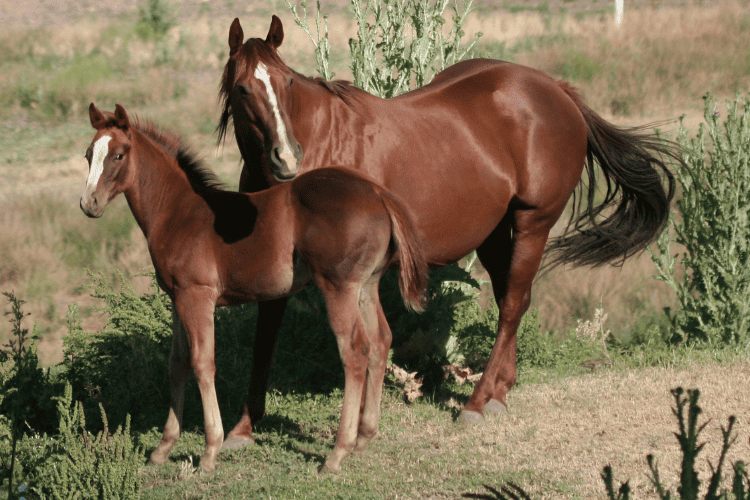
Thoroughbred and Quarter Horse are both used for a wide array of activities and purposes.
Thoroughbred horses are most commonly used for:
- Flat racing
- Steeplechase racing
- Dressage
- Cross-country
- Show jumping
Quarter Horses are, on the other hand, most suitable for the following activities:
- Western-style riding
- Cutting
- Rodeo
- Reining
- Work at ranch
- Trail riding
- Pleasure rides
Of course, both horses also make fantastic companions for any equestrian regardless of their professional or sports ambitions.
Price and Requirements
If you’re wondering how much these horses cost, the answer is not simple. The exact buying price of any equine depends on many variables, from location, bloodline, and age to genetic qualities, received training, and intended use.
Nevertheless, in general, a Thoroughbred will most likely cost you considerably more than a Quarter Horse.
In fact, Thoroughbreds are some of the most expensive horses. A championship-level animal typically costs between $100,000 and $300,000 – or even more. If you opt for a less lucrative option, still expect to spend at least $70,000 for a proper Thoroughbred.
Quarter Horses are much more accessible for budget-conscious equestrians. You can buy a decent horse of this breed for as little as $2,500 – $10,000, and even if you opt for an animal from a more prominent breeder, you probably won’t spend more than $25,000 – $50,000.
Moreover, these horses are also less demanding when it comes to specialized training, day-to-day care, and nutrition (learn how much does a horse eat in a day, if you’re interested in this topic).
Origins

The origin of the Thoroughbred can be traced to 17th-century England. It is closely connected to the following three stallion horse breeds imported from the East: Darley Arabian, Godolphin Arabian, and Byerley Turk.
These horses acquired exceptional athletic qualities through crossing with English mares, including extraordinary stamina, impressive speed, and seemingly endless energy.
The breed became particularly popular in the era when a horse race gained mass popularity. Thoroughbreds excelled in this area, so they quickly became demanded and valued worldwide and maintained their popularity until today.
Quarter Horse (also known as American Quarter Horse) was first bred in the early 17th century in colonial America by English settlers who crossed their imported horses of Arabian descent with Native American horses.
The name of this breed refers to its ability to excel in quarter-mile races (famous particularly in the 18th century). Later, however, these horses predominantly served on the Western American ranches, showing their great versatility and discipline at work.
American Quarter Horse Association (AQHA) was founded in 1940, contributing to the formalization and perseverance of the breed’s distinctive standards and characteristics. Quarter Horses are still one of the most popular horse breeds worldwide.
Rider Compatibility
As you’ve probably already assumed by now, I would not personally recommend a Thoroughbred to anyone who’s just starting with horses or lacks the ambition to train this beautiful horse for some serious competition.
However, if you’re a self-conscious jockey not limited by budget or time constraints, this energetic breed can accompany you on your path to success in many attractive disciplines.
A Quarter Horse is, in my opinion, an ideal choice for any recreational riders, beginners, or people interested in Western-style experiences like rodeo, ranch work, work around cattle, and so on.
This horse may also be suitable for people who are frightened of horses and hope to overcome their fear. I’ve witnessed a beautiful bond between a retired Quarter Horse and a woman recovering after an ugly horse-riding accident. These equines’ kindness, calm temper, and friendliness are simply unparalleled.
Thoroughbred and Quarter Horse Care

Taking care of a Thoroughbred is relatively demanding – especially if you want the animal to succeed in competitions or races. They require a well-balanced diet rich in nutrients, good hydration, and, most importantly, regular exercise and professional training.
Besides that, these energetic and sensitive horses also need proper mental stimulation. If they’re bored, they quickly become restless and agitated.
Of course, all of the above also applies to Quarter Horses. Nevertheless, this popular breed is generally more adaptable and less demanding. Still, you definitely should not neglect them in the sense of irregular training or unbalanced nutrition.
Once your animal starts suffering from metabolic issues (which is quite common), you’ll face stressful and expensive intensive veterinary care.
FAQs
Answer: Quarter Horse is the fastest horse that can sprint even quicker than a Thoroughbred. Nevertheless, it does not maintain the high speed for too long. Eventually, Thoroughbreds would most likely take over and win the race at a longer distance.
Answer: Whereas the American Quarter Horse is considered to be special mainly due to its calm temperament and versatility, a Thoroughbred is admired for its endless energy and great stamina. In my opinion, both are pretty special horse breeds deserving attention and adoration.
Answer: Both breeds can be wonderful companions, but based on my experience, a Quarter Horse is usually much calmer, less reactive, and generally better around small kids or inexperienced riders. This would be my first choice if you’re looking for a family horse.
Other Similar Horses
If you still can’t decide between Thoroughbreds and Quarter Horses, maybe you need to check some other options, too. Here are our guides to a few breeds that could interest you:

